The story of the Slocum disaster is truly a morbid one wherein negligence and ignorance resulted in the deaths of over a thousand poor souls on that fateful morning. People drowning due to the fact that they couldn't swim and were wearing heavy winter clothing, parents throwing their children overboard in an attempt to save them only to watch them sink like stones. Those who didn't drown in the East River that day burned to death on the boat.
The PS General Slocum was a passenger steamboat built in Brooklyn, New York, in 1891. The General Slocum was named for Civil War General and New York Congressman Henry Warner Slocum. She operated in the New York City area as an excursion steamer for the next thirteen years under the same ownership. During her service history, she was involved in a number of mishaps, including multiple groundings and collisions.
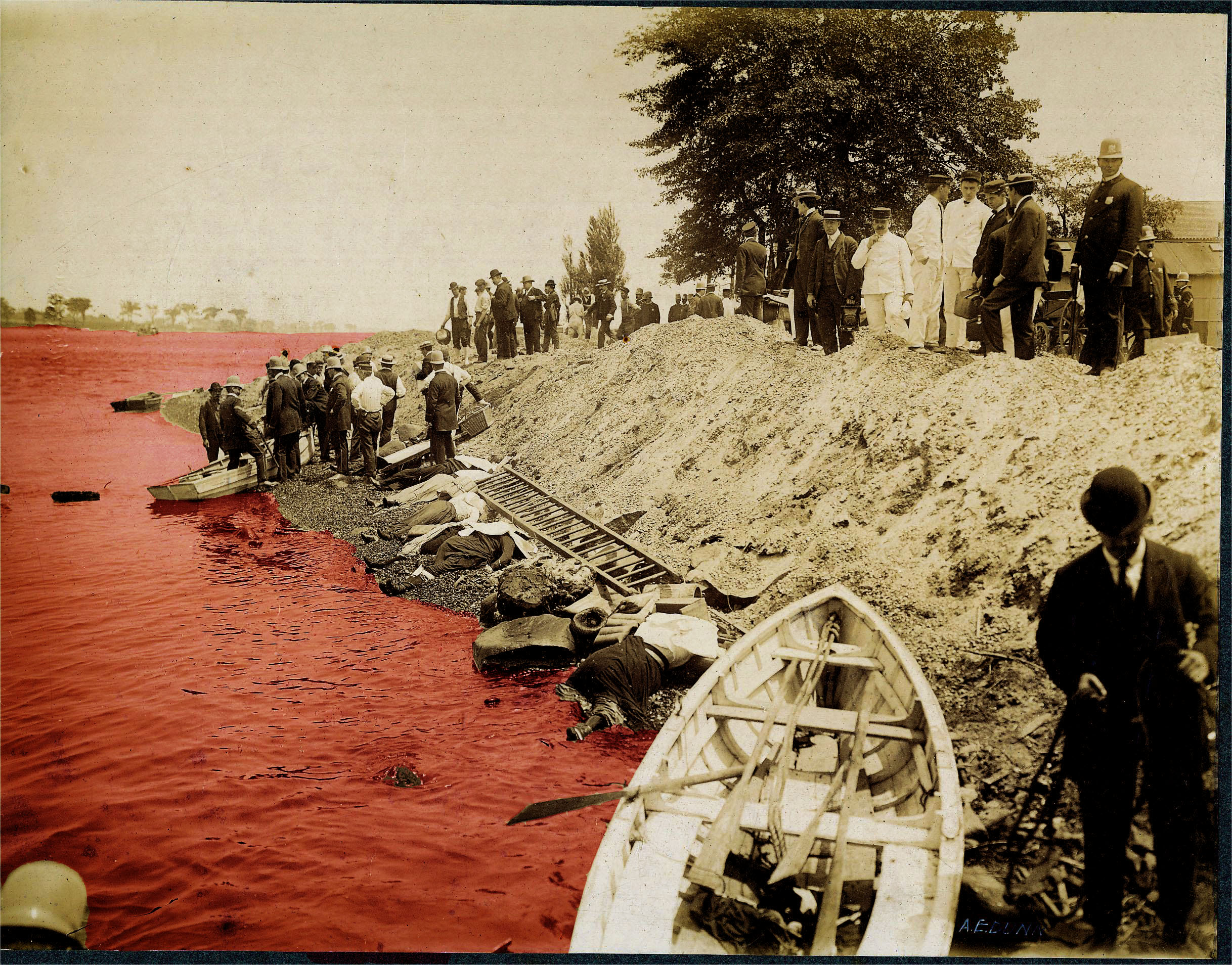
On June 15, 1904, the General Slocum caught fire and sank in the East River of New York City. At the time of the accident she was on a chartered run carrying members of St. Mark's Evangelical Lutheran Church (German Americans from Little Germany, Manhattan) to a church picnic. An estimated 1,021 of the 1,342 people on board died. The General Slocum disaster was the New York area's worst disaster in terms of loss of life until the September 11, 2001 attacks. It is the worst maritime disaster in the city's history.
The General Slocum worked as a passenger ship, taking people on excursions around New York City. On Wednesday, June 15, 1904, the ship had been chartered for $350 by St. Mark's Evangelical Lutheran Church in the Little Germany district of Manhattan. This was an annual rite for the group, which had made the trip for 17 consecutive years, a period when German settlers moved out of Little Germany for the Upper East and West Sides. Over 1,400 passengers, mostly women and children, boarded the Slocum, which was to sail up the East River and then eastward across the Long Island Sound to Locust Grove, a picnic site in Eatons Neck, Long Island.
The ship got underway at 9:30 a.m. As it was passing East 90th Street, a fire started in the Lamp Room in the forward section, possibly caused by a discarded cigarette or match. It was fueled by the straw, oily rags, and lamp oil strewn around the room. The first notice of a fire was at 10:00 a.m.; eyewitnesses claimed the initial blaze began in various locations, including a paint locker filled with flammable liquids and a cabin filled with gasoline. Captain Van Schaick was not notified until ten minutes after the fire was discovered. A 12-year-old boy had tried to warn him earlier but was not believed.
Although the captain was ultimately responsible for the safety of passengers, the owners had made no effort to maintain or replace the ship's safety equipment. The fire hoses had been allowed to rot, and fell apart when the crew tried to put out the fire. The crew had never practiced a fire drill, and the lifeboats were tied up and inaccessible. (Some claim they were wired and painted in place) Survivors reported that the life preservers were useless and fell apart in their hands. Desperate mothers placed life jackets on their children and tossed them into the water, only to watch in horror as their children sank instead of floating. Most of those on board were women and children who, like most Americans of the time, could not swim; victims found that their heavy wool clothing absorbed water and weighed them down in the river.
It has been suggested that the manager of the life preserver manufacturer placed iron bars inside the cork preservers to meet minimum weight requirements at the time. Many of the life preservers had been filled with cheap and less effective granulated cork and brought up to proper weight by the inclusion of the iron weights. Canvas covers, rotted with age, split and scattered the powdered cork. Managers of the company (Nonpareil Cork Works) were indicted but not convicted. The life preservers had been manufactured in 1891 and had hung above the deck, unprotected from the elements, for 13 years.
Captain Van Schaick decided to continue his course rather than run the ship aground or stop at a nearby landing. By going into headwinds and failing to immediately ground the ship, he fanned the fire. Van Schaick later argued he was trying to avoid having the fire spread to riverside buildings and oil tanks. Flammable paint also helped the fire spread out of control.
Some passengers jumped into the river to escape the fire, but the heavy women's clothing of the day made swimming almost impossible and dragged them underwater to drown. Many died when the floors of the overloaded boat collapsed; others were battered by the still-turning paddles as they tried to escape into the water or over the sides.
By the time the General Slocum sank in shallow water at North Brother Island, just off the Bronx shore, an estimated 1,021 people had either burned to death or drowned. There were 321 survivors. Five of the 40 crew members died. The captain lost sight in one eye owing to the fire. Reports indicate that Captain Van Schaick deserted the Slocum as soon as it settled, jumping into a nearby tug, along with several crew. Some say his jacket was hardly rumpled, but other reports stated that he was seriously injured. He was hospitalized at Lebanon Hospital.